| When did it happen? |
I have pondered this important question since 1986 and have considered dates between 2,800 and 28,000 B.C.
Different timelines are conceivable according to which evidence is used or rejected. Based on a preponderance of evidence against it, I discard long half-life radioisotope dating of rocks foundational to the conventional timeline, which itself rejects radiocarbon dates of dinosaur bones.
1. Carbon-14 dates
Ma (Mega-annum) means millions
of years ago
The 26-hour-long Shock Dynamics event is bracketed between widely separated markers: the "End of dinosaurs" around 30,000 years ago and "White Sands footprints" around 22,000 years ago.
End of dinosaurs – ranging from 39,000 to 22,000 years
before present - https://www.newgeology.us/presentation48.html
White Sands footprints - Bennett, Matthew R. et al. 23
September 2021. Evidence of humans in North America during the Last Glacial
Maximum. Science, Vol. 373, No. 6562, pp. 1528-1531 DOI:10.1126/science.abg7586
Younger Dryas event - Sweatman, Martin B. July 2021. The
Younger Dryas impact hypothesis: review of the impact evidence. Earth-Science
Reviews, Vol. 218, 103677 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103677
This calibration curve shows that the proportion of Carbon-14 in the atmosphere compared to today has varied over the range of measurable radiocarbon dating - about 55,000 years:
From:
Heaton, T. J. et al. 5 November 2021. Radiocarbon: A key
tracer for studying Earth’s dynamo, climate system, carbon cycle, and Sun.
Science, Vol. 374, No. 6568 DOI:10.1126/science.abd7096 Note:
IntCal13 is data from 2013, IntCal20 is data from 2020
Researchers involved with assembling the IntCal20 calibration curve described its limitations:
"[T]he IntCal20 curve itself is created in two linked sections. Firstly, we create the more recent part of the curve (extending from 0 back to approximately 14,000) which is predominantly based upon dendrodated tree-ring determinations. Secondly, we create the older part of the curve (from approximately 14,000 back to 55,000) which is based upon a wider range of material, e.g. corals, macrofossils, forams, speleothems as well as five floating tree-ring chronologies."
"These alternative sources of data are typically not direct measurements of the atmosphere but instead are offset due to marine reservoir effects and dead carbon fractions. Further, their true calendar ages are quite uncertain and can only be estimated. For the corals and speleothems these estimates are obtained via U-Th dating."
"Within the IntCal database, many of the determinations have calendar ages which are not known absolutely. This is particularly the case as we progress further back in time and calendar age estimates are constructed from uranium-thorium (U-Th) dating (for example speleothems and corals); varve counting; and palaeoclimate tuning/tie-pointing. Furthermore, in the case of several of the floating tree-ring sequences, we have only a relative set of calendar ages and no absolute age estimate."
"The speleothem records contain carbon obtained from dripwater which has passed through old limestone and so is a mixture of atmospheric CO and dissolved old (dead) carbon that has no activity. The offset in radiocarbon age this creates is called a dead carbon fraction (dcf) and is specific to the speleothem. Similarly, the marine records have an atmospheric offset called a marine reservoir age (MRA) that arises due to both the limited gas exchange with the atmosphere and ocean circulation drawing up deep old carbon. These MRAs are location specific and vary over time."
"These offsets must be estimated within curve construction to adaptively synchronize the different records. Notwithstanding the above attempts to accurately model dcf and MRA, we recognized that there was further variation in the offsets over time we were not able to fully capture."
"[T]he entire timescale for Hulu Cave is not the same as the Suigetsu or Cariaco timescale. As a consequence, all of these individual datasets may show the same overall features but at slightly different times. We require our method to recognize that these different timescales may need to be aligned, within their respective uncertainties, to keep these shared features. This requires us to shift multiple ages jointly by stretching/squashing the timescales accordingly." -Heaton, Timothy J., Maarten Blaauw, Paul G. Blackwell, Christopher Bronk Ramsey, Paula J. Reimer, E. Marian Scott. August 2020. The IntCal20 Approach to Radiocarbon Calibration Curve Construction: A New Methodology Using Bayesian Splines and Errors-in-Variables. Radiocarbon, Vol. 62, No. 4: IntCal20: Calibration Issue, pp. 821-863 DOI:10.1017/RDC.2020.46
The dips in the C14/C12 ratio are likely due to the release of volumes of Carbon-12 into the atmosphere that had been buried and lacked significant Carbon-14. Since Carbon-14 continues to be produced in the upper atmosphere, the system rebalances steadily over time, but without taking anywhere near as long as IntCal says. Uranium-thorium (U-Th) dating, which I discount, “stretches” the IntCal timeline. Here I “squash” it and indicate several catastrophic events that could be associated with major undulations in the calibration curve. The timeline for each event covers onset through rebalance.
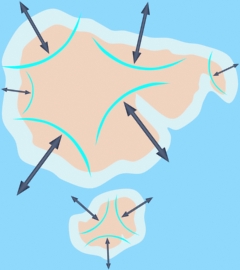
2. Sequence of Earth events
|
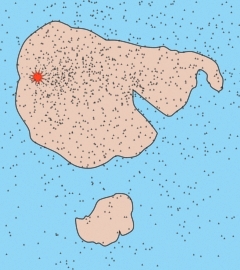
1.2 billion years ago - The planetoid Theia has a grazing collision with Earth, forming the Moon. 1.1 billion years ago - Earth is fully accreted 1 billion years ago - A moderate size meteorite impacts Earth’s northern hemisphere forming Antar, an island of continental crust. 0.9 billion years ago - A large asteroid strikes Earth, forming a magma ocean over 40% of Earth’s surface while cutting Antar in two, sending half of it sliding to Earth’s southern hemisphere. The seafloor briefly boils, forming thousands of seamounts. A thick vapor canopy forms above the surface. The magma ocean differentiates and solidifies into continental crust. 30,000 years ago - A swarm of small meteorites pummels the Moon and Earth, collapsing the vapor canopy. Earth is heavily flooded, producing the Phanerozoic strata up to the Cretaceous. The Chicxulub impact occurs, spreading a wide iridium-filled fallout blanket. The Shock Dynamics impact occurs, dividing the protocontinent, building mountain chain, forming subduction zones, and depositing the Cenozoic (Tertiary) strata. "Then the flood swept over", recorded in the Sumerian King List. Using the estimated date for Gilgamesh, that flood occurred around 3000 BC. |
It is my experience that many creationists have mistakenly combined evidence from two separate catastrophic events (a global flood and splitting the crust into separate continents) into one - a global flood. My own preference is for Young Biosphere Creation. Here is more on the sequence of events from a creationist point of view:
|
|
|
Before the Flood, a water vapor canopy covers the Earth. There is a veil of ice clouds in the mesosphere. Earth's atmosphere is dense (2 or 3 bars at sea level). Many creatures grow to gigantic sizes, and men can live up to 1000 years. |
|
|
or |
|
The "Age of Dinosaurs" |
|
|
|
This environment ends when a long swarm of mostly small meteorites begins striking the Moon and Earth. The bombardment goes on for forty days, causing the vapor canopy to collapse and rain down on the Earth. Much of the atmosphere is lost. |
|
|
|
Noah takes some of each kind of animal living around him into the Ark. Meteorites hitting the ocean raise plumes of water that Noah calls "fountains of the deep". On land, some impacts make large craters such as Vredefort and Sudbury, and unleash the Siberian flood basalts. All creatures run for cover. |
|
|
|
The Flood of Noah |
|
|
|
Before the Flood, there is much sand and mud around the edges (shelf) of the protocontinent and East Antarctica. During the Flood, massive waves of ocean water wash onto the land, depositing sediment from the continental shelf. Each wave then retreats, but rising water brings the next wave farther inland. As atmospheric pressure falls from 2 or 3 bars to 1, much calcium carbonate precipitates from the sea water by "degassing", forming limestone and cementing the sand and mud. These become the thick sedimentary rock layers that are full of "Paleozoic" and "Mesozoic" fossils. |
|
|
|
The first waves bring in sea creatures living in the shallow waters of the continental shelf, as well as land animals living near the ocean. These lowest fossil layers are "Paleozoic". |
|
|
|
Subsequent waves overwhelm and bury the dinosaurs. These fossil layers are "Mesozoic". |
|
|
|
Once the vapor canopy is gone and the atmosphere is thinner, more sunlight reaches the surface and rainbows can appear. |
|
|
|
The flood waters only had to rise hundreds of feet above sea level to cover the hills, rather than many thousands of feet to cover the mountains we have today. Over a period of months, the water filtered down through the new layers of sediment, revealing dry land to Noah. The sediments eventually hardened into sandstone, limestone, and shale sedimentary rocks thousands of feet thick. The filtered flood waters provide the water table under continents from which we draw well water. |
|
|
|
Chicxulub
impact |
|
|
|
The "Age of Mammals" |
|
|
|
The Shock Dynamics
event |
|
|
|
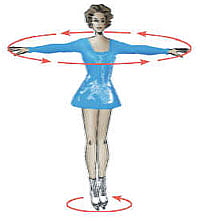
Much of the continental crust moves away from the equator and towards the poles during the Shock Dynamics event (especially India, Asia, Southeast Asia, Antarctica, and Alaska). Like a figure skater spinning faster as she pulls her arms in, the reduced weight at the equator increases the speed at which Earth rotates on its axis. So days become slightly shorter, and a year grows from 360 to 365.25 days (a 1.46% change). Also, the redistribution of weight at the surface adds a small wobble to the Earth as it spins. |
|
|
|
Ice Age |
|
|
|
Younger
Dryas catastrophe |
|
|
|
Survivors, scattered throughout the world, slowly rebuild civilization. Their stories reflect similar memories of ancient times. Sages watch the night sky for signs of another assault from the stars. |
|
|
|
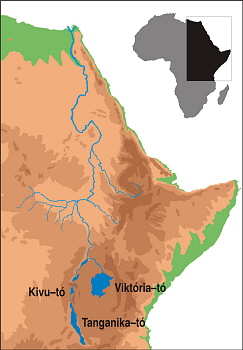
Before the Shock Dynamics event there was no Nile River. Uplift of East Africa around Lake Victoria and where the Horn of Africa was forced inland (Ethiopia) directed river flow to the north to empty into the Mediterranean Sea. |
|
|
|
This allowed the civilization of ancient Egypt to arise, with life centered on the Nile. |
3. Sumerian complication
|
|
Similarities between the ancient Mesopotamian Flood story and the story of Noah suggest that they refer to the same event. In fact, the Sumerian account of kingship identifies a deluge as dividing its history (Marchesi, 2010, p. 232). Archaeologists have found evidence of catastrophic flooding in Mesopotamia dating in the range of 3500 to 2600 BC, with a preference for around 2900 or 3000 BC (Raikes, 1966; Kramer, 1967). This opens the possibility that there were three separate events that creationists have rolled into one: destruction of the dinosaurs, the Shock Dynamics event, and a civilization-destroying flood in Mesopotamia. |
Marchesi, Gianni. January 2010. The Sumerian King List and the Early History of Mesopotamia. University of Rome "Wisdom", Department of Historical, Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences of Antiquity, Near East Section, Notebook V, Rome 2010. file:///C:/Users/jmfis/Downloads/The_Sumerian_King_List_and_the_Early_His.pdf
Raikes, R. L. Spring 1966. The Physical Evidence for Noah's Flood. IRAQ, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 52-63 DOI:10.2307/4199795
Kramer, Samuel Noah. 1967. Reflections on the Mesopotamian Flood; The Cuneiform Data New and Old. Expedition, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 12-18 https://www.penn.museum/documents/publications/expedition/PDFs/9-4/Reflections.pdf
Commentary:
Wake up to the numbers
Neanderthals mated with modern humans; there was not much difference between
them. - Dediu,
Dan, Stephen C. Levinson. 2018. Neanderthal language revisited:
not only us. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 21, pp.
49-55 DOI:10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.01.001

Recorded history of modern humans is less than 6,000 years. Conventional science says Neanderthals were in Europe and Asia from 130,000 to 40,000 years ago; that’s 90,000 years. This is where they went in 90,000 years:
So people like us were primitives in caves, never spread across the world, and made no technological progress for 90,000 years? Ridiculous!
Conventional science throws huge numbers around without pausing to think how dumb it sounds.
Most Tyrannosaurus
rex’s lived in what is now western North America (Laramidia) when it was isolated by
water.
The remains of 32 Tyrannosaurus rex's have been found by paleontologists. Conventional science says T. rex existed for about 2 million years, so a German researcher calculated the total number that would have lived in Laramidia during 2 million years using a reasonable estimate of the T. rex life cycle: 1.7 billion Tyrannosaurus rex's; 32 fossil remains. Claiming 2 million years for T. rex is super ridiculous! - Griebeler, Eva M. April 2023. Vital statistics, absolute abundance and preservation rate of Tyrannosaurus rex. Palaeontology, Vol. 66, No. 2, e12648 DOI:10.1111/pala.12648
This is from the LiveScience website: "...where are all the T. rex bones? If Griebeler's predictions are correct, it means that we have only found the remains of 0.0000002% of these giant dinosaurs. This is an important question that requires further research, Griebeler and Marshall said." (Eva Griebeler is an evolutionary ecologist at the Johannes Gutenberg University at Mainz, Germany, and Charles Marshall is a paleontologist at the University of California, Berkeley.) https://www.livescience.com/animals/dinosaurs/17-billion-tyrannosaurus-rexes-walked-the-earth-before-going-extinct-new-study-estimates
These are just two of many examples. There is no reality in the numbers conventional science routinely reports, so don't expect those numbers here.
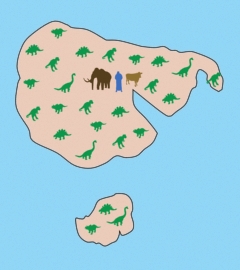
Dinosaurs - undivided
on the protocontinent
There used to be a belief that there
were "differences between the Cretaceous dinosaur faunas of
Laurasia and Gondwana, with 'characteristic' taxon sets identified
in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres." Northern Pangea
is called Laurasia; southern Pangea is called Gondwana. But
the discovery "of an Australian Cretaceous spinosaurid, in
combination with other recent Gondwanan discoveries of clades previously
thought to be restricted to Laurasia (e.g. tyrannosauroid and dromaeosaurid
theropods, ankylosaurid ankylosaurs, iguanodontian ornithopods),
provides evidence for the cosmopolitan [or widespread] distribution
of many dinosaur clades during the Early-'middle' Cretaceous."
Likewise, researchers have found "many formerly 'Gondwanan'
clades in Laurasia, such as rebbachisaurid sauropods, and abelisauroid
and carcharodontosaurian theropods." "Analyses have
identified sister-group relationships between Cretaceous genera
that cross the Gondwanan/Laurasian 'divide': for example, the Australian
neovenatorid theropod Australovenator is the sister-taxon of the
Japanese Fukuiraptor, and the Australian titanosaurian sauropod
Diamantinasaurus is most closely related to Opisthocoelicaudia from
Mongolia." So finding the first spinosaurid theropod
dinosaur in Australia "is part of a growing body of evidence
that seriously undermines the prevalent view of pronounced north-south
differences between Early-'middle' Cretaceous dinosaur faunas."2
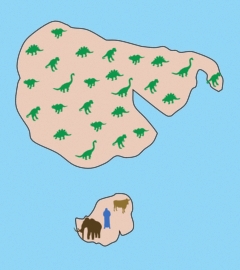
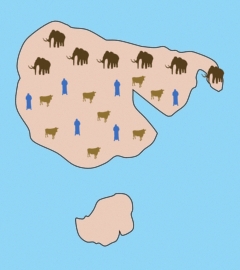
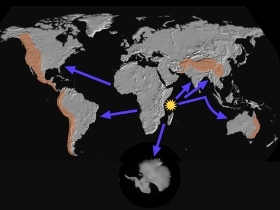
Mammoths
The Shock Dynamics
theory explains the mass extinction of woolly mammoths and other
large mammals found in post-Flood sediments. The theory
shows how the protocontinent (similar to Pangaea
of Plate Tectonics) was shattered by a giant meteorite impact and
the pieces flung to their present locations over about 26 hours.
Before the impact, what is today North America and northern
Asia were below 60 degrees latitude. Overnight they were violently
thrown northward. Cross-continental wind storms buried
millions of mammoths deep in loose wind-blown soil, while hundreds
of thousands more were swept into the ocean onto continental shelves.
The Siberian environment quickly changed from temperate
grasslands to arctic tundra with permafrost.
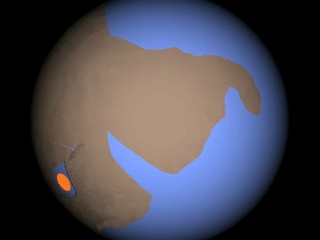
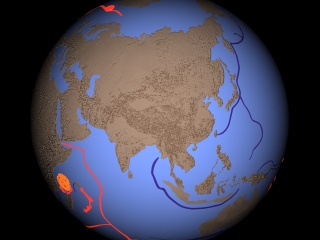
Creationist researcher Michael Oard has studied the extinction of the woolly mammoth for many years. Here are some of his findings.8 "There are probably millions of mammoths buried in the permafrost of Siberia alone. The mammoths are found with a wide variety of other mammals, large and small, many of which were grazers. They lived in a grassland environment with a long growing season, mild winters, very little permafrost, and a wide diversity of plants -- quite different from the climate in the region today." "They were buried in the dust storms that deposited the loess blankets found in those regions today. Some were entombed in a standing position."

Siberia, Alaska, and the Yukon Territory of Canada, together with the surrounding shallow ocean (Bering Strait), are called Beringia. "Mammoths are commonly found in surficial sediments from western Europe eastward through northern and eastern Asia, Alaska and the Yukon. Mammoth remains are also found on some of the islands in the Bering Sea and are dredged from the shallow continental shelves surrounding Beringia. Enormous numbers of ice age mammals, most commonly mammoths, are dredged up from the unconsolidated sediments of the North Sea by trawlers." "Mammoth and mastodon teeth have been dredged from 40 sites along the continental shelf off the eastern US in water up to 120 meters deep." "It would be conservative... to conclude that several million mammoths are buried in Beringia."
"Woolly mammoths are not the only fossil mammals found in the permafrost of Beringia. There are a wide range of other mammals, large and small, that accompany the mammoths. These include the woolly rhinoceros, wolf, fox, lion, brown bear, camel, deer, ground sloth, pika, wolverine, ferret, ground squirrel, moose, reindeer, yak, musk ox, giant beaver, lemming, porcupine, coyote, skunk, mastodon, antelope sheep, voles, hare and rabbit, plus many species of birds, rodents, horses, and bisons."
"There is abundant evidence that the woolly mammoths in Siberia, Alaska and the Yukon died after the Flood." The surface sediment "lies upon hundreds of meters of consolidated sedimentary rock that a large majority of creationists would attribute to the Flood."
As a result of "great tectonic and volcanic upheaval, the stratosphere would have held great quantities of dust and aerosols." "Thus sunlight would have been partially reflected back to space from the volcanic products trapped in the stratosphere. Less sunlight would have meant cooler land surfaces." "Evaporation would be much greater at mid and high latitude than today due to the much warmer water. Copious evaporation close to the ice sheets would have been most favourable for their rapid growth." Oard is probably not aware of the Shock Dynamics theory and, along with most creationists, believes the "great tectonic and volcanic upheaval" occurred during the Genesis Flood rather than long afterward, as presented here. However, the effects are just as relevant.
Oard writes, "I believe the secret to their demise and burial can be found in the type of sediment surrounding the woolly mammoths." "The vast majority of the animals are found in the 'yedomas' of Siberia and the 'muck' of Alaska. The yedomas, a Yukut term, are hills 10-20 meters, sometimes up to 60 meters, high." "There is now general agreement that the yedomas and muck are loess -- a wind-blown silt! Much data support the wind-blown origin of this sediment." "Thus it seems likely that the mammoths in Beringia were mostly killed and buried by dust storms." "The permafrost would then move upward after the loess was deposited and rapidly freeze the remains, thus accounting for the rapid burial." "Copious wind-blown dust even occurs in the ice age portion of the Greenland and Antarctic ice cores."

"Today, Siberia is well known for its bitterly cold winters." "Siberia today is in the permafrost zone where up to a meter of the surface melts in the summer. Water pools on the surface forming massive bogs and muskegs, making summer travel difficult, if not impossible, for man and beast."8

If only two mammoths survived the Flood, was 300 years enough time to build the population of millions that we find buried? Yes. If we use the elephant life-cycle as a model, a 13 year doubling rate would produce a population at least as large as that which was buried.
Other
large mammals
Animals
today live in some parts of the world and not in others. In
the same way, before the Shock Dynamics event, large mammals occupied
different regions of the protocontinent. So along with the
woolly mammoth, in Europe and northern Asia the woolly rhinoceros,
giant deer, and cave bear are found buried. In North America
it is the columbian mammoth, mastodon, saber-tooth cat, giant ground
sloth, shasta ground sloth, and yesterday's camel. In South
America it is the litoptern, notoungulate, and glyptodon. And
in Australia it is the giant kangaroo, marsupial lion, diprotodon,
short-faced kangaroo, and giant short-faced kangaroo.7
Caves
After the Flood, receding flood waters would
have carved long caves in the
newly deposited limestone. Several hundred years later waves
carried carcasses of animals deep into these caves during
the upheaval of the Shock Dynamics event. The book Cataclysm!1
has a chapter (10) describing the bodies of all kinds of mammals
carried deep into limestone caves throughout the world. "The
shattered remains of countless 'Pleistocene' (Ice Age) animals and
plants were deposited both north and south of the equator, in limestone
caves and rock-fissures". "These caves, via narrow
fissure-like tortuous passages, often penetrate solid rock for horizontal
and vertical distances sometimes exceeding several hundred feet,
are intersected by separate fissure systems, and are globally very
numerous." "Most of the remains retrieved from these
apertures have been deposited in great confusion, with normally
incompatible kinds of animals lying in unnaturally close juxtaposition.
Often accompanying these organic masses are both rounded and
angular stones of dissimilar composition and, less frequently, sizable
boulders. All these objects are usually enveloped and united
by consolidated muds, earths or hard breccias". They
report on caves found in Europe, Asia, North and South America,
and Australia. Occasionally human remains are there as well.
Meteorites and the Flood
Evidence of meteorite impacts is found throughout the world in different sedimentary rock layers that creationists associate with the Noahic Flood. Dr. Andrew Snelling elaborates on this in an Answers in Genesis article: https://answersingenesis.org/the-flood/did-meteors-trigger-noahs-flood/
Tektites
|
|
|
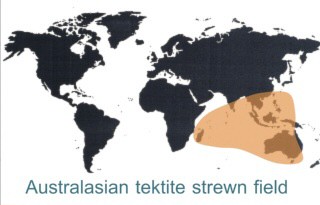
The Australasian tektite strewn field also appears to be a post-Flood feature (even in uniformitarian literature, from the Pleistocene at 700,000 years before present). A source crater for this, the largest strewnfield by far, has never been found. The fallout area fits the Shock Dynamics impact, just north of Madagascar. |
Sediment runoff
|
|
|
Continental crust weathers over time, leaving soil, sand, and clay sediment. This is why volcanic islands in the Pacific, are not just islands of barren rock. Rivers and rain wash sediment out to sea, and it settles on the continental slope. |
Calcium carbonate from seawater
Surface ocean water is saturated
with the elements that form calcium carbonate, and magnesium is
present as well. The removal of carbon dioxide from seawater
is called degassing. Degassing is a primary method for calcium
carbonate precipitation, and it is enhanced by the agitation of
crashing waves. In this model, the extended global meteorite
bombardment collapses the vapor canopy and Earth loses much of its
original atmosphere. The greatly lowered atmospheric pressure
causes rapid degassing of the surface waters of the ocean. As
the waves roll over the continent, calcium carbonate and calcium-magnesium carbonate precipitate into the sediment carried by the
waves, forming limestone, sandstone, mudstone, dolomite, etc., depending
on the contents of the waves. These carbonates are the principal
"glue" that binds sedimentary rock minerals together.
On the other hand, the much later Shock Dynamics impact did not remove enough atmosphere to lower atmospheric pressure, so calcium carbonate was not produced in vast amounts as before. Cross-continental waves did deposit sediment, but only a little calcium carbonate was released by wave agitation. That is why Cenozoic layers are mostly loose sediment, unlike the hard Paleozoic and Mesozoic rocks. "Cenozoic sediments can be recognized in the field because for the most part they are just that, sediments (rocks composed of unconsolidated [loose] materials). Where lithified, Cenozoic sandstone is usually friable [crumbly] and shale is mechanically weak." --Rance, Hugh. 1999. The Present is the Key to the Past. Queensborough Community College Press, online textbook, page 213. "The sedimentary rocks of the Cenozoic era are, for the most part, quite loose and uncompacted; it is relatively rare to find hard rocks, such as so generally characterize the older formations." --Scott, William Berryman. 1914. An Introduction To Geology. The MacMillan Company, New York, Chapter XXXV.
Folding and faulting
The flat layers of sediment
laid down by the Flood were folded and faulted long after the
Flood by Shock Dynamics tectonics. The sediment has since hardened
into rock.


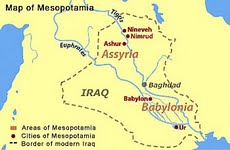
Mesopotamia
No dinosaur fossils
or footprints have been found in Mesopotamia (Iraq).
Noah
Noah reported only
what he saw. Many have speculated that what Noah called "fountains
of the deep" were vents or cracks in the seafloor from which
water flowed to raise the ocean. But Noah could not see below
the surface of the ocean. He could see plumes of water
shooting high in the air and falling. Noah did not know the
maximum depth of the flood waters. The draft of the ark was
likely half its height (half of 30 cubits is 15 cubits). Once
the flood rose 15 cubits and lifted the ark to float on the water,
all he could add was that the waters covered the highest ground
(Genesis 7:20). He looked all around, and water covered everything.
The animals Noah saved were those that lived in his region.
That included all sorts of birds. Most important to
his livelihood were cattle, and they are mentioned specifically
twice (Genesis 7:14, 7:21).
Dinosaur death
pose
So many dinosaur fossils have been found with their
neck arched way back that this "opisthotonic posture"
is often referred to as the "dinosaur death pose". Most
are found in sediment laid down by water. To see if water
was a factor, an experiment was conducted with dead chicken carcasses
and a bucket of water. "Within seconds of submerging
the chicken, its head became drawn backwards into a position similar
to the death pose. We repeated this procedure six times with
fresh and frozen chickens, altering the conditions to rule out confounding
variables. Our results were consistent." This supports
the idea that dinosaurs all over the world were victims of a very
large flood. --Cutler, Alicia, Joshua Cotton, Dr. Brooks
Britt, Department of Geological Sciences, Brigham Young University.
The classical death pose as a function of aqueous deposition. NCUR
2012 (The National Conference on Undergraduate Research, March 29-31
2012, Weber State University, Ogden, Utah).

Ararat
The ark ran aground on high terrain.
However, at the time Ararat was not the desolate region of mountains
over 10,000 feet high that exists now. It is implausible
that people or animals could have survived if they had to descend
those rugged heights. Yet everyone dispersed easily
and quickly throughout the land; the hills must have been relatively
low before the Shock Dynamics event.

Meteorite bombardment
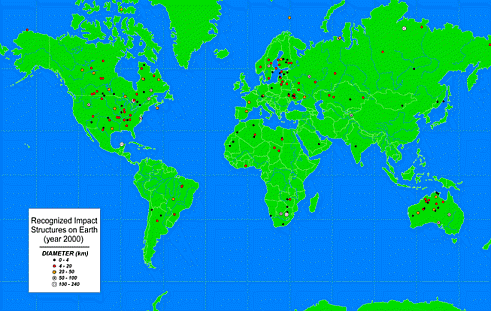
So far, 190 impact crater structures have been found on Earth; 42 are 20 km or more in diameter. It is likely that many others exist in remote regions that have been less studied. We would expect there to be hundreds more on the seafloor since oceans cover most of the planet, yet hardly any have been found. Water depth may be a factor, and they may be difficult to discern. Impact craters are spread throughout the geologic column. For uniformitarians, that means billions of years. For creationists, that means bombardment during the catastrophic events that laid down the strata. So in this model of Earth history, both the Flood and the Shock Dynamics event must have been associated with global meteorite bombardments. See Dr. Andrew Snelling's article on this.
"The Moon and all the terrestrial planets were resurfaced during a period of intense impact cratering." "Only a sudden injection of impacting objects into the terrestrial planet zone could account for the abrupt end of the intense bombardment; thus, this event has been named the Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB), or sometimes the Lunar Cataclysm." "The lunar cataclysm hypothesis postulates that the intense bombardment of the Moon lasted only a very short period of time." "Therefore the LHB was a catastrophic event." "The LHB affected the entire inner solar system, not just the Moon."
Crater size distribution and chemical analyses show that "the source of the LHB impactors was the main asteroid belt and that the dynamical mechanism that caused the LHB was unique in the history of the solar system and distinct from the processes that produce the flux of objects currently hitting planetary surfaces."
"The terrestrial planets have been impacted by two populations of objects that are distinguishable by their size distributions. Population 1 is responsible for the LHB, and Population 2 is responsible for impacts since the LHB period."
"The size distribution of Population 2 projectiles is the same as that of the near-Earth asteroids and quite different from that of the LHB projectiles." Strom, Robert G., Renu Malhotra, Takashi Ito, Fumi Yoshida, David A. Kring. 16 September 2005. The Origin of Planetary Impactors in the Inner Solar System. Science, Vol. 309, pp. 1847-1850.
Of course, the uniformitarian timescale places the LHB nearly 4 billion years ago, and the "very short period of time" is 20 to 200 million years! Nevertheless, the catastrophic nature of the LHB and the distinct populations of craters are still important observations for creationists.
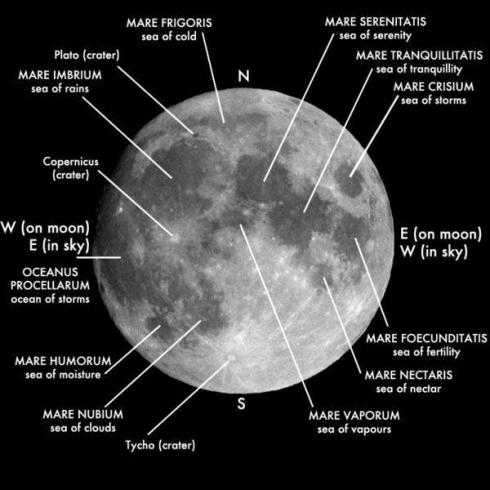
Some Population 1 craters were later obliterated by a few very large impacts on the nearside of the Moon. These huge impacts leveled (modified) parts of the surface inside and beyond the impact craters, forming "basins", such as the Imbrium, Crisium, and Serenitatis basins. No doubt similar large asteroids hit Earth as well. Head III, James W., Caleb I. Fassett, Seth J. Kadish, David E. Smith, Maria T. Zuber, Gregory A. Neumann, Erwin Mazarico. 17 September, 2010. Global Distribution of Large Lunar Craters: Implications for Resurfacing and Impactor Populations. Science, Vol. 329, pp. 1504-1507.
The following sequence of events seems reasonable:
1) A portion of the swarm of LHB asteroids fell on the Earth, initiating the Flood of Noah by collapsing the vapor canopy.
2) 531 years later, a handful of very large asteroids arrived in such a tight group that they formed basins on only the nearside of the Moon. The giant meteorite that divided the protocontinent on Earth in the Shock Dynamics model was part of this group.
3) Near-Earth asteroids have been striking the Earth and Moon ever since.
British researchers Clube and Napier have identified what they believe are the shattered remains of a giant asteroid on an Earth-intercept orbit. An unknown number of these pieces have already collided with the Moon and Earth, such as the famous 1908 Tunguska event on Earth and the 1178 AD impact that made the Bruno crater on the Moon. Their list of the remaining pieces includes seven asteroids and two comets (all a few kilometers in diameter); Taurid and Orionid micrometeor streams; and the Stohl dust stream. Clube and Napier suggest that, following the breakup of the giant asteroid, the Moon and Earth were bombarded with a swarm of the pieces and have encountered the diminished remains ever since. They also warn that today there are probably 1000 - 2000 "Apollo asteroids", each over a kilometer in diameter, in potential Earth-intercept orbits. --Clube, Victor, Bill Napier. The Cosmic Winter. 1990. Basil Blackwell Ltd., Oxford, UK. 307 pages.
Radiometric
dating
The tenuous
chain of assumptions and documented errors of radiometric dating
is well known to creationists. Even the venerated zircon has
been compromised, because "zircon grains are readily infiltrated
by fluids"11.
However, some creationists
invoke an accelerated rate of radioactive decay during Creation
and the Flood to explain apparent ages of millions and billions
of years. This resort to supernatural intervention has no
scriptural support, is unnecessary, and opens up many problems with
physics and biology.
What is actually measured in radiometric dating are the so-called parent and daughter elements, such as Uranium-238 and Lead-206 or Thorium-232 and Lead-208. The parent element may decay into many other unstable elements on the way to its stable daughter element. For example, Thorium-232 decays into 9 different elements on its way to Lead-208, and all of these should be present if a rock sample has indeed sat undisturbed long enough to decay to its stable daughter (as long as any parent element remains).
One of the unknowns in geology is how elements accumulated in the different layers of the Earth, and even how the continental crust we live on formed. There are theories, of course, but each has problems. All mainstream ideas involve Plate Tectonics producing continental crust little by little through multiple melting-eruption-hydration-subduction cycles.
My hypothesis is that continental crust was produced during the impact that created the Moon, and was metamorphosed during the Shock Dynamics event. The Moon-forming impact melted the Earth where it hit, forming a "magma ocean" from the oceanic (basaltic) crust at the surface to the lower mantle. The affected area was about 41% of the surface of the Earth, the area covered by continental crust. A veteran researcher makes an important point concerning Earth's main heat-producing "radioactive elements K, U, and Th. The continental crust contains about 35% of the total 'bulk silicate earth' (BSE) supply. But as the crust is only 0.5% of the mass of the BSE, it is enriched by a factor of about 70 in K, U, and Th relative to BSE. This implies that at least 35% of the BSE passed through whatever melting processes eventually formed the continents."15 That it is close to the 41% of the Earth covered by continental crust is encouraging.
During melting, these elements, along with the other radioactive elements, their daughter elements, and many others, efficiently gathered into liquids throughout the affected mantle and rose within magma to the surface. These elements were not dispersed randomly throughout the crust. They fractionated (separated from the magma) according to their atomic structure. Since parent and daughter elements are closely related in structure, they would tend to fractionate together as continental crust rock formed.5 Therefore, measuring how much of each element is in a piece of continental crust measures more than how much of a parent element has decayed into its daughter element. It also measures the abundance of these elements in the source mantle from which they came. In the old-Earth/young-biosphere (plants and animals) model of Gorman Gray, the age of the rocks of the Earth are unknown and could be quite old. The source mantle could have been full of the whole range of radioactive decay elements, from both original accretion and radioactive decay. Thus samples taken from the continental crust would be useless in determining its age.
Each time large-scale melting occurs, parent and daughter elements rise and become more concentrated near the surface. That seems to make the surface rocks appear older to radiometric dating techniques, reversing the order in which they actually formed. The first melting event (accretion of the Earth) formed oceanic basalt. The next melting event (Moon-forming impact) formed continental crust, which is "dated" as older than oceanic basalt. The last melting event (Shock Dynamics impact) caused stress-melting that formed cratons, which are "dated" as older than the rest of the continental crust. Additionally, meteorites in the swarm that initiated the Flood melted continental crust according to their size, speed, and angle of impact. So a large impact such as Vredefort melted a lot of crust, yielding a much older radiometric "date" than smaller impacts that hit at the same time.
The discovery of measurable Carbon-14 in fossilized organic material does, however, put an upper limit on the age of the biosphere: "Given the short Carbon-14 half-life of 5730 years, organic materials purportedly older than 250,000 years... should contain absolutely no detectable Carbon-14." "Almost without exception, when tested by highly sensitive accelerator mass spectrometer (AMS) methods, organic samples from every portion of the Phanerozoic [(fossil)] record show detectable amounts of Carbon-14!" AMS is capable of measuring Carbon-14 levels of less than 0.01 percent modern carbon (pmc). The mean value for fossil samples is 0.29 pmc, while samples without fossils have a mean value of 0.06 pmc. "In terms of the standard geological timescale, all these samples should be equally Carbon-14 dead."3 Dates determined by other radiometric methods for similar samples are far older, up to hundreds of millions of years. But the discovery of protein and soft tissue in a dinosaur fossil thought to be 80 million years old13, confirming previous finds14, adds more doubt to these supposed vast ages. Dinosaur bones have been dated with Carbon-14 (click on pdf).
Without a verifiable way to determine absolute age, researchers in catastrophic geology can only judge relative age; lower rocks were laid down before higher rocks. That is to say, lower catastrophes occurred before higher ones, with rapid deposition of perhaps thousands of feet of sediment in a single catastrophic event, and each new event may have removed some of the previously deposited sediment by scouring. The rock record would not reveal the time between events.
Geologic
column
The geologic
column was invented before the theory of evolution. It assigned
rocks to places in the column mainly according to the fossils found
in the rocks. One of the popular myths of the geologic column
is that the Earth is covered like a layer cake by successive strata.
In reality, the coverage is quite spotty. As depicted
in this map, if the world were covered in the youngest strata it
would be light brown all over, without any of the oldest (red)
rock showing. That means up to hundreds of millions of years
of sedimentary deposits, according to the uniformitarian scenario,
are missing from much of the Earth's surface. These are not
just canyons cut by rivers down to lower strata, but large portions
of all continents.
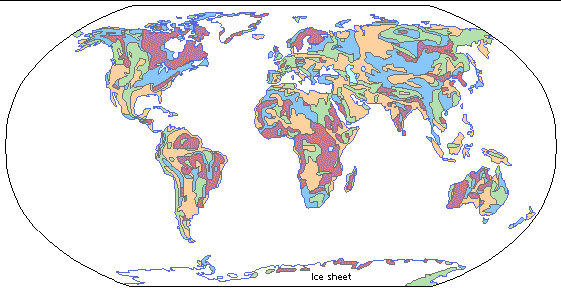
From
Grolier Online Atlas - Geology
Fossils
That distinctive
layers do exist is generally accepted. Theorizing begins
with how the fossils got there. In the uniformitarian view,
as long as a type of creature such as a trilobite existed, occasionally some
of them would be fossilized, accumulating in layer upon layer of
sediment deposited gradually over millions of years. Thus
the point at which trilobite fossils diminish in number or disappear
from higher rock layers is considered the time of extinction; all
the layers below record "trilobite life as usual". The catastrophist
view is that until a catastrophic event occurred there was virtually
no fossilization going on. Then suddenly whole series of sedimentary
layers were laid down. They hardened into rock and fossilized
the creatures buried in them. Thus the point at which trilobite
fossils diminish in number or disappear from higher rock layers
marks the end of their extinction event, which includes all the
layers piled up below that point. The difference is important.
Which is right?
Unburied carcasses disintegrate quickly, so fossilization requires rapid burial. The very slow accumulation of sediment on the floor of a lake or ocean in the uniformitarian scenario could hardly cover even a leaf. Covering a dinosaur would take millennia, so local floods, landslides, or quicksand-like pits are postulated. Yet many strata extend over vast regions. Large numbers of creatures and plants are found fossilized together, often broken in pieces or piled up. The uniformitarian scenario does not fit reality. On the other hand, the catastrophist scenario requires no special pleading, particularly for the action of huge tsumani-style waves of water. The work of French geology researcher Guy Berthault3 has shown that multiple layers of graded beds of sediment can be deposited simultaneously by a single wave, and that lamination is affected by current speed. On a large scale, this would produce a whole series, or sequence, of strata from an individual wave. Deposition by wave after wave over an area could lead to repetitive groups of sequences.
Here is where the broad range of fossils are found in the geologic column.
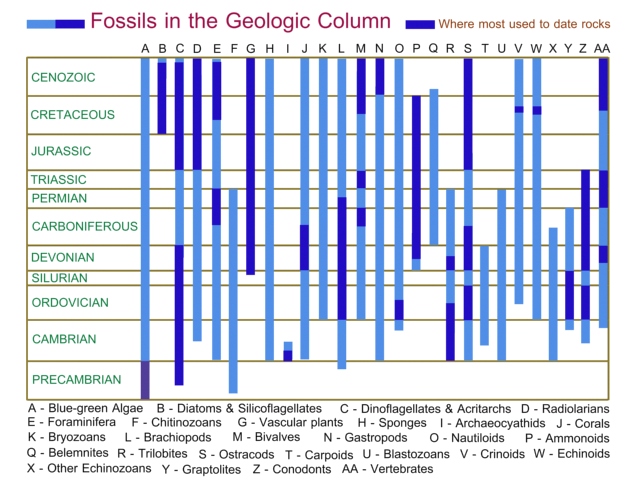
After
Fenton, Carroll Lane, Mildred Adams Fenton. 1989. The Fossil
Book: A Record of Prehistoric Life. Doubleday, New York. p.
65.
Mass extinctions
Mass extinctions
have been located by researchers throughout the geologic column.
Many are shown here, with the length of the lines indicating
the level of devastation.
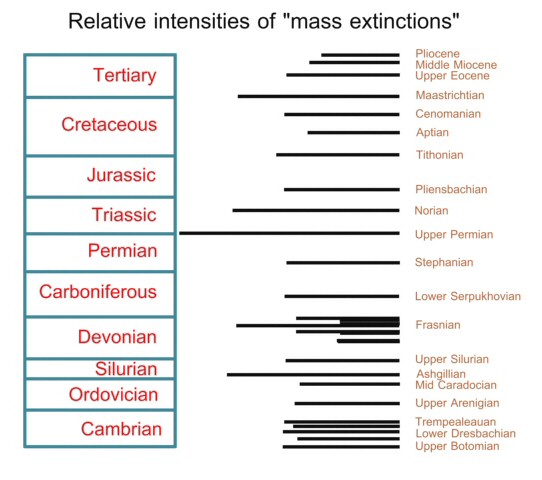
After
Hallam, A., P.B. Wignall. 1997. Mass Extinctions and Their Aftermath.
Oxford University Press, UK. p. 5
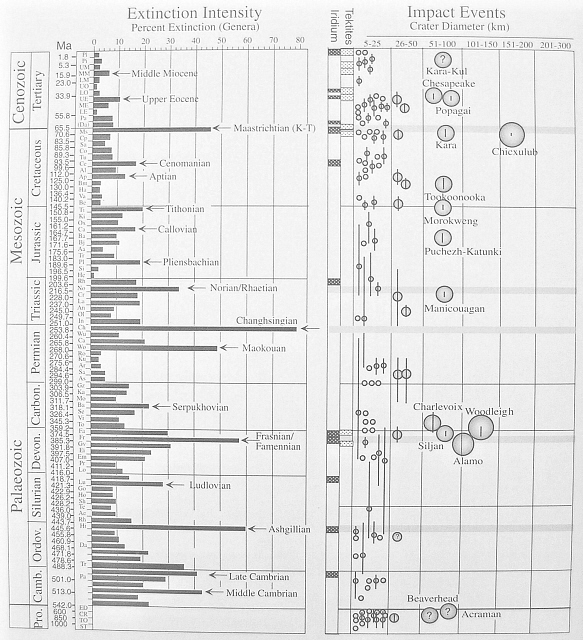
From
Keller, Gerta. 2008. Impact stratigraphy: Old principle, new reality.
in Evans, K.R., Horton, J.W., Jr., King, D.T., Jr., and Morrow,
J.R., eds. The Sedimentary Record of Meteorite Impacts: Geological
Society of America Special Paper 437, pp. 147-178.
A very candid book, The Origin of Mountains9, was published in 2000. The authors, Cliff Ollier and Colin Pain, are two PhD Australian researchers in geomorphology with experience in geology before and after the Plate Tectonics revolution. While generally supporting Plate Tectonics, they list 17 problems with that theory. Some of these are: 1) "The total length of spreading sites is three times longer than that of subduction sites." 2) "The North America plate rides indiscriminately over the North Pacific (and other) plates with no regard to spreading sites, plate margins, or transform faults." 3) "If subduction is the cause of mountain building, why did mountain uplift occur mainly in the last 5 million years, while subduction is supposedly a continuous process that worked over the past 50 to 200 [million years] in different parts of the world?" 4) "Subduction fails to explain why there is a period of still-stand [erosion], when land was extensively planated [ie. made smooth] before the period of mountain uplift on a global scale." 5) "Plate tectonics as a general principle has been enormously helpful in many aspects of geology, but its practitioners have neglected the ground surface, and have often been uncritical in their time scales. The geomorphology of mountains and their recent origin make plate tectonics an improbable mechanism for mountain building."9 Of particular interest here is that most mountain uplift is relatively recent, and that globally the surface was made smooth prior to the raising of mountains. They also say that "Uplift occurred over a relatively short and distinct time. Some earth process switched on and created mountains after a period with little or no significant uplift. This is a deviation from uniformitarianism. The mountain building period is generally relatively short. It does not appear to be on the same time scale as granite intrusion which takes tens of millions of years, or plate tectonics which is continuous. The same rapid uplift occurs in areas where hypotheses such as mantle plumes do not seem appropriate. We do not yet know what causes this short, sharp period of uplift, but at least the abandonment of naive mountain building hypotheses might lead to further realistic explanations."9 Their list of mountain ranges mostly includes the "collision" and "brake" mountains of Shock Dynamics which are raised in the latter part of this 26-hour event. The sudden and unique nature of the mountain building they describe is characteristic of the effects from a shock impulse of global proportions.
The Appalachians exemplify impulse mountains raised at the beginning of the Shock Dynamics model. Folding of these mountains was caused by pressure from the shock wave initiated by the giant meteorite impact east of Africa. This is borne out by a specialist in Appalachian geology who wrote, "maximum orogeny [mountain building] took place in a linear core belt... These rocks, and any floor on which they may have rested, were as if gripped and squeezed between the jaws of a giant vise, and at the same time heated up enough to become quite plastic and to stew in their own juice, in the fluids released as they transformed into mineral assemblages." "...for me the vise is not a metaphor but a fairly exact model. Thus the evidence of intense shortening perpendicular to the length of the chain, not only in the folded marginal belts but also in the central core belt, is too clear for me to doubt that there was not only confining but directed pressure, the greatest compressive stress being consistently directed roughly horizontally across the orogenic belt." "Compression then relaxed, and the thickened crust rose isostatically to form mountains and has continued to do so ever since."12 As a believer in Plate Tectonics, he cannot find a mechanism in the crust that could do this, and imagines mantle convection must be involved.
The smooth planing of many continental surfaces prior to mountain building is also interesting. Sliding landmasses would naturally cause waters to overrun the continents and send giant waves rushing across oceans to opposite shores. Here at last we find a cause for the sediment-bearing waves that catastrophists have long recognized as the source of strata of limestone, dolostone, sandstone, shale, etc. thousands of feet thick, as well as for scouring and planing-smooth vast continental surfaces.
All continental flood basalts occurred above the Permian. The most massive by far of these outpourings of molten rock onto the surface of continents was the Siberian flood basalt flow, right at the Permian-Triassic boundary. It is likely that this flow occurred before the Shock Dynamics event, perhaps at the end of a previous global catastrophe.
The Cretaceous-Tertiary (K/T) boundary includes the famous termination of dinosaur fossil deposition. The massive Deccan Trap continental flood basalt outpouring is associated with this boundary. Its location in western India makes it reasonable to connect it to the separation of India from Africa following the giant meteorite impact. Also, the apparent global fallout of iridium (Ir) at the K/T boundary suggests an end to high-energy activity. The thin layer of clay in which the iridium spike (concentration) is found is significant because it indicates a thick global dust cloud, an expected consequence of a giant impact. The persistent work of Gerta Keller in recent years has shown that the Chicxulub impact was not connected to K/T extinction. Her placement of the Chicxulub impact 300,000 years before the K/T extinction6 is meaningful to uniformitarians but not for catastrophists, who place at least the whole Mesozoic section in a single event.
However, another finding is noteworthy: "Throughout Central America, the Chicxulub glass spherules have never been observed together with the iridium anomaly or the mass extinction but always well below it."6 Glass spherules, or shocked quartz, are traceable chemically to a specific meteorite impact; iridium fallout is not, thus far. Hundreds of impact craters have been found on land, some larger than Chicxulub. The question naturally arises, why are there not more large iridium spikes found in the geologic column? After studying about 8,000 rock samples, researchers at Los Alamos Laboratory concluded "The K/T Ir anomaly is far stronger than anything we have found in our analysis of thousands of sedimentary-rock samples from throughout the fossil record. Our work on Deccan basalts and other forms of volcanism have convinced us that eruptive processes were not the source of the Ir anomaly."10 Keller proposes that a larger impact than Chicxulub yielded the K/T Ir anomaly.6
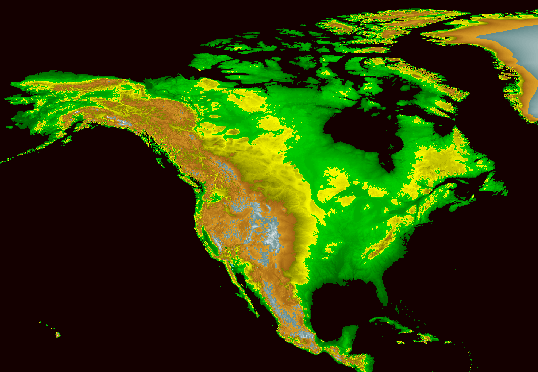
Elevation
map from National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA website
**********
References
1. Allan, D.S., J.B. Delair. 1997. Cataclysm! Compelling Evidence of a Cosmic Catastrophe in 9500 B.C. Bear & Co., Rochester, Vermont.
2. Barrett, Paul M., Roger B.J. Benson, Thomas H. Rich, Patricia Vickers-Rich. Published online June 21, 2011. First spinosaurid dinosaur from Australia and the cosmopolitanism of Cretaceous dinosaur faunas. Biology letters, doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.0466.
3. Baumgardner, John R., D. Russell Humphreys, Andrew A. Snelling, Steven A. Austin. 2003. Measurable 14C in Fossilized Organic Materials: Confirming the Young Earth Creation-Flood Model. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Creationism, R.L. Ivey (editor), pp. 127-142.
4. Berthault, G. 2002. Analysis of Main Principles of Stratigraphy on the Basis of Experimental Data. Lithology and Mineral Resources, Vol.37, No. 5, pp. 442-446.
5. Brimhall, Jr., George H. 1987. Preliminary fractionation patterns of ore metals through Earth history. Chemical Geology, Vol. 64, pp. 1-16.
6. Keller, Gerta, et.al. 2004. More evidence that the Chicxulub impact predates the K/T mass extinction. Meteorites & Planetary Science, 39, Nr 7, pp. 1127-1144.
7. Lister, Adrian, Paul Bahn. 2007. Mammoths: Giants of the Ice Age. University of California Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles.
8. Oard, Michael J. (2001?) The extinction of the woolly mammoth: was it a quick freeze? 11 pages, open source online.
9. Ollier, Cliff, Colin Pain. 2000. The Origin of Mountains. Routledge, London. pp. 296-307.
10. Orth, C. J., et.al. 1990. Iridium abundance patterns across bio-event horizons in the fossil record. Geological Society of America Special Paper 247, pp. 45-59.
11. Rasmussen, Birger, Ian R. Fletcher, Janet R. Muhling, Courtney J. Gregory, Simon A. Wilde. December 2011. Metamorphic replacement of mineral inclusions in detrital zircon from Jack Hills, Australia: Implications for the Hadean Earth. Geology, Vol. 39, No. 12, pp. 1143-1146.
12. Rodgers, John. 1970. The Tectonics of the Appalachians. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. p. 224.
13. Schweitzer, Mary H., et. al. 1 May 2009. Biomolecular Characterization and Protein Sequences of the Campanian Hadrosaur B. canadensis. Science, Vol. 324, 626-631.
14. Schweitzer, Mary Higby, Jennifer L. Wittmeyer, John R. Horner. 2007. Soft tissue and cellular preservation in vertebrate skeletal elements from the Cretaceous to the present. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Vol. 274, pp. 183-197.
15. Sleep, Norman H. 2005. Evolution of the Continental Lithosphere. Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Vol. 33, pp. 369-393.
2005
- 2026
John
Michael Fischer
www.newgeology.us